Vector Cartesian Form
Vector Cartesian Form - Find the cartesian equation of this line. Web cartesian components of vectors. The cartesian form of the equation is formed by eliminating the constant λ from the vector equations. Recall that the general form of the equation of a straight line in two dimensions is 𝑎 𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0. The cartesian coordinate system is very convenient to use in describing displacements and velocities of objects and the forces acting on them. Web let’s first consider the equation of a line in cartesian form and rewrite it in vector form in two dimensions, ℝ , as the situation will be similar for a plane in three dimensions, ℝ. Aqa a level further maths: Web = + , this is known as the cartesian form in 2d space. What are the different vector forms? Ab→ = 1i − 2j − 2k ac→ = 1i + 1j a b → = 1 i − 2 j − 2 k a c → = 1 i + 1 j.
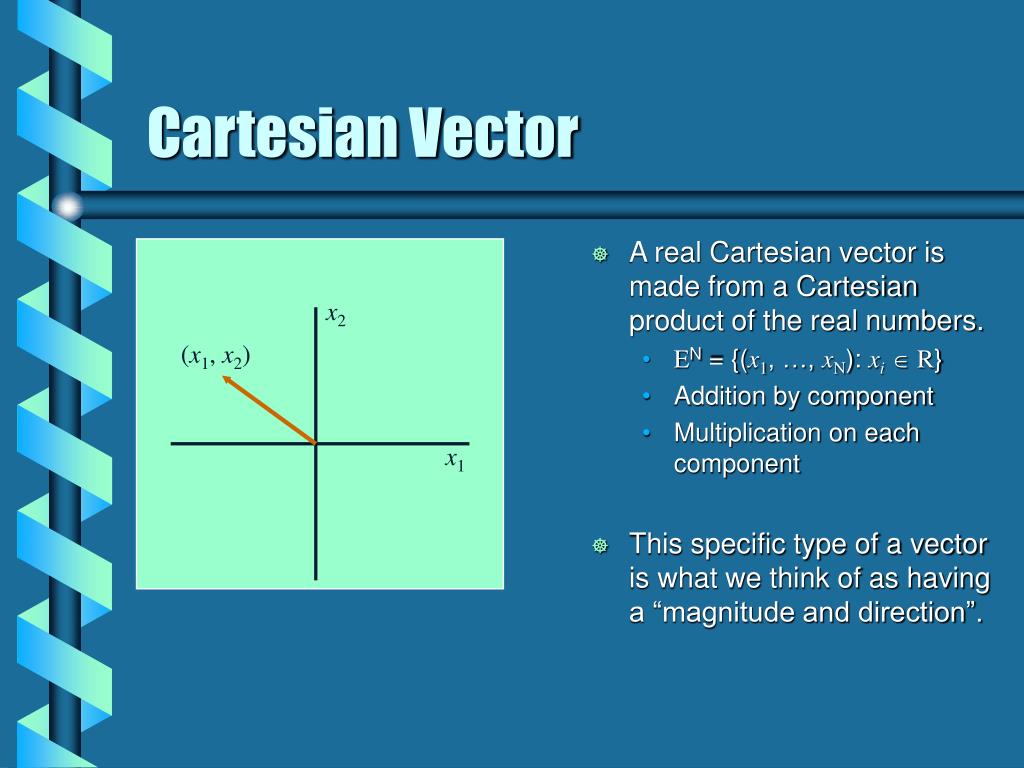
Both forms could be compared to the cartesian equation of a 2d. Key point 5 x y o p i j (a, b) r a b figure 26 the position vector of p with coordinates (a,b) is r = −→ op = ai+bj unlike most vectors, position vectors cannot be. Any vector may be expressed in cartesian components, by using unit vectors in the directions of the coordinate axes. Both forms could be compared to the cartesian equation of a 2d line. The cartesian coordinate system is very convenient to use in describing displacements and velocities of objects and the forces acting on them. ⋅n^ r → ⋅ n ^ = a → ⋅ n ^ or, r. Vector form of the equation of a line.
R = a + t d. Line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector. Web there are two formulas for getting a vector equation of a line: The formula for finding the vector equation of a line is. Where r is the position vector of any point on the line.
Line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector. For example, ( 3, 4). Web as the need for handling complex geometries in computational fluid dynamics (cfd) grows, efficient and accurate mesh generation techniques become paramount. In component form, we treat the vector as a point on the coordinate plane, or as a directed line segment on the plane. So you should proceed as. Web = + , this is known as the cartesian form in 2d space.
The cartesian form of equation of a line passing through the point ( x 1, y 1, z 1) and having the direction cosines a, b, c is. Web the cartesian form of representation for a point is a(a, b, c), and the same in vector form is a position vector \(\vec oa = a\hat i + b\hat j + c\hat k\). Both forms could be compared to the cartesian equation of a 2d. In this unit we describe these unit vectors in two dimensions and in three dimensions, and show how they can be used in calculations. Let us understand the use of vector form to represent a point, a line, a plane, with the help of examples, faqs.
The point on the line a is similar to the “+c” part. Review all the different ways in which we can represent vectors: Considered graphically, there's another way to uniquely describe vectors — their magnitude and direction : Vector form of the equation of a line.
In Component Form, We Treat The Vector As A Point On The Coordinate Plane, Or As A Directed Line Segment On The Plane.
Web the cartesian equation of a plane is given in the form. A is the position vector of a known point on the line. Web a point can be represented in cartesian form as a(x, y, z) and in vector form is it is represented as $\vec{oa} = a\hat{i} + b\hat{j} + c\hat{k}$. We can plot vectors in the coordinate plane by drawing a directed line segment from the origin to the point that corresponds to the vector's components:
The Vector Equation Of A Line Is R → = 3 I ^ + 2 J ^ + K ^ + Λ ( I ^ + 9 J ^ + 7 K ^) , Where Λ Is A Parameter.
Ab→ = 1i − 2j − 2k ac→ = 1i + 1j a b → = 1 i − 2 j − 2 k a c → = 1 i + 1 j. Considered graphically, there's another way to uniquely describe vectors — their magnitude and direction : Line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector. The formula for finding the vector equation of a line is.
The Cartesian Coordinate System Is Very Convenient To Use In Describing Displacements And Velocities Of Objects And The Forces Acting On Them.
Use this formula when you know the position vector a of a point on the line and a direction vector d; Web now consider the special case when r represents the vector from the origin o to the point p(a,b). Web converting vector form into cartesian form and vice versa (practice) | khan academy. This is given in the formula booklet.
Use This Formula When You Know The Position Vector A Of A Point On The Line And A Direction Vector D.
R ⇀ = a ⇀ + λ b ⇀ w h e r e , a ⇀ = x 1 i ⏞ + y 1 j ⏞ + z 1 k ⏞ b ⇀ = a i ⏞ + b j ⏞ + c k ⏞. Web the cartesian form of representation of a point (x, y, z) can be written in vector form as \(\vec a = x\hat i + y\hat j + z\hat k\). Key point 5 x y o p i j (a, b) r a b figure 26 the position vector of p with coordinates (a,b) is r = −→ op = ai+bj unlike most vectors, position vectors cannot be. ⋅n^ = d r → ⋅ n ^ = d.