Rc Circuit E Ample Problems
Rc Circuit E Ample Problems - Web a simple explanation of an rc circuit. In this section we see how to solve the differential equation arising from a circuit consisting of a resistor and a capacitor. Discussion 2 µf 100 kω. Learn what an rc circuit is, series & parallel rc circuits, and the equations & transfer function for an rc circuit. A 50 v ac is applied across an rc series network. I = ɛ/r = 1.5 v/150 kω = 0.01 ma. We solve for the total response as the sum of the forced and natural response. Web the rc circuit has thousands of uses and is a very important circuit to study. A simple rc circuit as shown in figure 20.8.1 20.8. T is the elapsed time since the application of the supply voltage;
A basic rc circuit, initial state. When charged, the potential difference across the terminals of the capacitor is 9v 9 v. 922k views 6 years ago electronic circuits. Vs is the supply voltage; Consider the circuit shown in figure 8.4.1. 1) rc circuit review 2) equations for rc 3) time response of rc circuits 4) rc filters. Rc circuits click here to see the solutions.
922k views 6 years ago electronic circuits. Discussion 2 µf 100 kω. How long wiil the circuit take to reach steady state (approximately). (b) the maximum charge on the capacitor. 1) rc circuit review 2) equations for rc 3) time response of rc circuits 4) rc filters.
This is called the natural response. Learners read how total productive maintenance can prevent breakdowns, defects, and a variety of other losses. What factors contribute to the capacitance of a capacitor? Web in an rc circuit connected to a dc voltage source, voltage on the capacitor is initially zero and rises rapidly at first since the initial current is a maximum: Becomes smaller, the capacitance goes up. We solve for the total response as the sum of the forced and natural response.
Not only can it be used to time circuits, it can also be used to filter out unwanted frequencies in a circuit and used in power supplies, like the one for your computer, to help turn ac voltage to dc voltage. Web solve those problems easily. Rc circuits click here to see the solutions. Not only can it be used to time circuits, it can also be used to filter out unwanted frequencies in a circuit and used in power supplies, like the one for your computer, to help turn ac voltage to dc voltage. The time constant for an rc circuit is τ = r ⋅ c.
This physics video tutorial explains how to solve rc circuit problems with capacitors and resistors. What factors contribute to the capacitance of a capacitor? Chapter 28, objective question 7 conceptual question 6 problems 37, 41, 43, 63. How long wiil the circuit take to reach steady state (approximately).
Web In An Rc Circuit Connected To A Dc Voltage Source, Voltage On The Capacitor Is Initially Zero And Rises Rapidly At First Since The Initial Current Is A Maximum:
A capacitor of capacitance 1000 μf is connected to a resistor of resistance 150 kω and a battery of 1.5 v in series. Web a simple explanation of an rc circuit. A 50 v ac is applied across an rc series network. Web the rc circuit has thousands of uses and is a very important circuit to study.
The Rc Step Response Is A Fundamental Behavior Of All Digital Circuits.
Chapter 28, objective question 7 conceptual question 6 problems 37, 41, 43, 63. Normally, the problem will just ask you one part of them. How long wiil the circuit take to reach steady state (approximately). The instant power is applied, the two capacitors appear as short circuits.
Find The Maximum Current That Flows Through The Resistor While Charging.
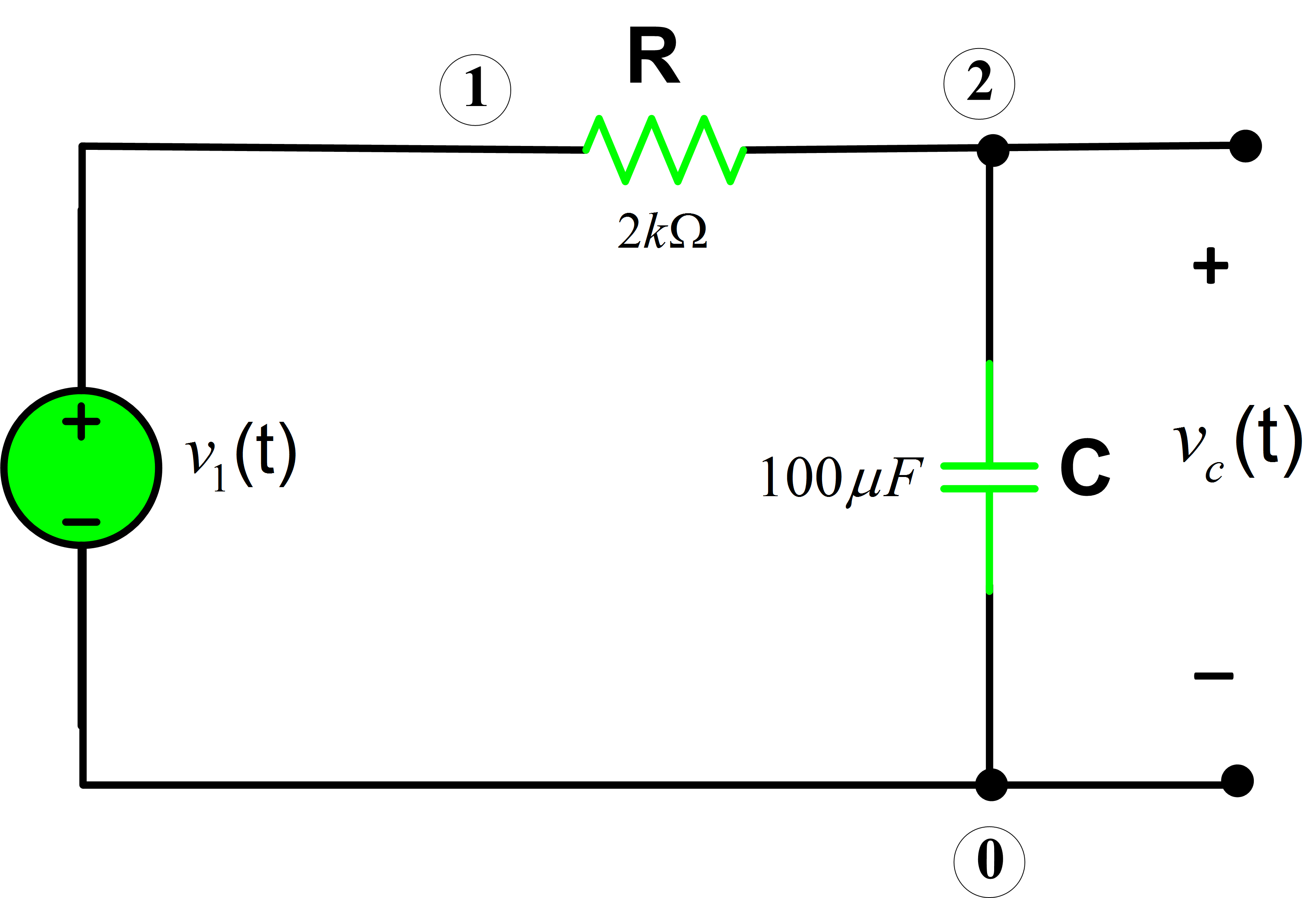
We also discuss differential equations & charging & discharging of rc circuits. Web rc circuits text section 28.4 practice: The currents in r1, r2, and r3 are denoted as i1, i2, and i3, respectively. Note the use of a voltage source rather than a fixed current source, as examined earlier.
The Time Constant For An Rc Circuit Is Τ = R ⋅ C.
T is the elapsed time since the application of the supply voltage; Web solve those problems easily. Given this equivalent, we can see that shorting c2 c 2. (b) the maximum charge on the capacitor.
![Solved (3) RC Circuit a) The RC circuit shown in [Fig 11]](https://i2.wp.com/d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media/a1e/a1e2d11a-364d-4d3c-b1ac-fb9e561f5c8c/php5RIUFM.png)