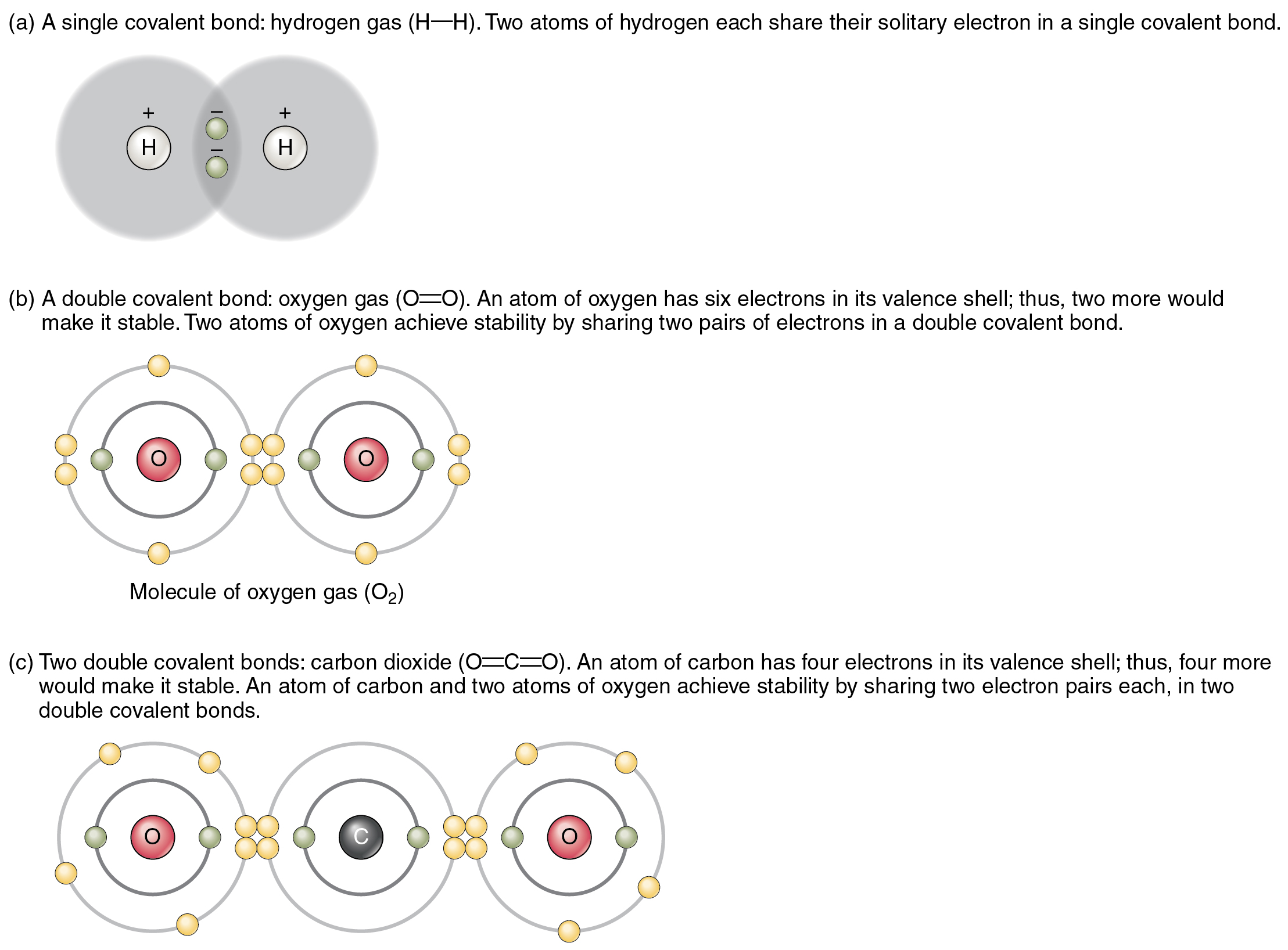
How Many Bonds Can Carbon Form With Other Elements
How Many Bonds Can Carbon Form With Other Elements - If not, then what are the other elements can also do this? Carbon occurs as a variety of allotropes. Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Web the number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Calcium atoms are shown as white. Carbon gets many of its properties from its ability to sustain up to four bonds at a time. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom (figure 1). Will form either one, two, three or four covalent bonds with other atoms.
Web carbon most often forms a covalent bond with other atoms. Carbon can form single, double, or triple. If not, then what are the other elements can also do this? By forming four covalent bonds, carbon shares four pairs of electrons, thus filling its outer energy level and achieving stability. In this ground state carbon has 2 unpaired p electrons which can form 2 bonds. Web carbon is unique among the elements in its ability to form strongly bonded chains, sealed off by hydrogen atoms. Web each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds close covalent bonding a covalent bond is formed by a shared pair of electrons.
When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called hydrocarbons. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called hydrocarbons. Carbon can form four covalent bonds. In this ground state carbon has 2 unpaired p electrons which can form 2 bonds. An example of this is co carbon monoxide.
These hydrocarbons, extracted naturally as fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), are mostly used as fuels. Web carbon is unique among the elements in its ability to form strongly bonded chains, sealed off by hydrogen atoms. Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. The electrons are thus equally. With other carbon atoms the carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings Carbon can form either 2 or 4 bonds.
Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. The ground state electron configuration is 1s22s22p2. Carbon can form four covalent bonds. This allows carbon to fill its outer energy level and make the carbon atom more. A bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms.
Group 5a (15) elements such as nitrogen have five valence electrons in the atomic lewis symbol: However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. When it bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds called hydrocarbons.
Web These Four Electrons Can Be Gained By Forming Four Covalent Bonds, As Illustrated Here For Carbon In Ch 4 (Methane).
Web moreover, of all the elements in the second row, carbon has the maximum number of outer shell electrons (four) capable of forming covalent bonds. Web carbon most often forms a covalent bond with other atoms. Carbon can form either 2 or 4 bonds. Carbon can form single, double, or triple.
If You've Ever Seen A D4 Or A Caltrop, You've Seen The Shape Of The Bond Sites On A.
Carbon’s ability to form bonds with four other atoms goes back to its number and configuration of electrons. The electronegativity value for carbon (c) and hydrogen (h) is 2.55 and 2.1 respectively, so the difference in their electronegativity values is only 0.45 (<0.5 criteria); Web carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. Web carbon can form up to four covalent bonds and thus share four pairs of electrons with other atoms.
Therefore, It Can Form Four Covalent Bonds With Other Atoms Or Molecules.
(other elements, such as phosphorus [p] and cobalt [co], are able to form five and six covalent bonds, respectively, with other elements, but they lack carbon’s ability to bond indefinitely with. This leaves carbon with six electrons in its outer shell. Web the carbon atom has unique properties that allow it to form covalent bonds to as many as four different atoms, making this versatile element ideal to serve as the basic structural component, or “backbone,” of the macromolecules. These four elements are widely used when it comes to drawing lewis structures at introductory chemistry level.
Carbon Forms Strong Double And Triple Bonds With A Number Of Other Nonmetals, Including N, O, P, And S.
However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. Web carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Form long c −c chains, with differing substitution along that chain.