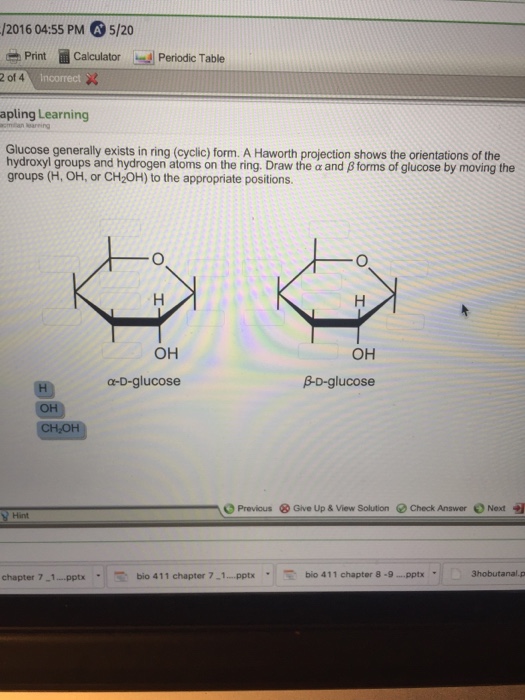
Glucose Generally E Ists In Ring Form
Glucose Generally E Ists In Ring Form - The process is catalyzed by acid, since hemiacetal formation is catalyzed by acid. Linear glucose has four chiral carbons (pointed to by the red arrows). Forms of glucose by moving the groups (h, oh, or ch2oh) to the appropriate positions. Draw the î± and î² forms of glucose by placing the groups (h, oh, or ch2oh) in the appropriate positions. These two forms always exist in equilibrium. A haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and hydrogen atoms on the ring. Glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Note that a new asymmetric centre is formed on cyclization, at c1. Hence glucose forms a six membered ring structurally similar to that of pyran, whilst fructose forms a five membered ring similar to furan. Look at the orientation of the hydroxyl group at c2.
Web sugars in aqueous solution exist in an equilibrium between the linear form and the ring form, which is formed by intramolecular attack by a hydroxyl group on the carbonyl. Look at the orientation of the hydroxyl group at c2. Draw the a and the b forms of glucose by placing the groups (h, oh, or ch,oh) in the appropriate positions. Glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. When that happens, there are two possible orientations. Whereas glucose and galactose are predominantly found in the β anomeric form, mannose is most frequently found as α anomer. Draw the α and β forms of glucose by moving the groups (h, oh, or ch _2 2 oh) to the appropriate positions.
Web the most prevalent form for most carbohydrates is a ring. Glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Web glucose is usually present in solid form as a monohydrate with a closed pyran ring (dextrose hydrate). Web glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Is the alpha or the beta form “really” glucose?
The process is catalyzed by acid, since hemiacetal formation is catalyzed by acid. One of the oxygens farther along the chain can reach around and bond to the carbon in the c=o at the head of the chain. Whereas glucose and galactose are predominantly found in the β anomeric form, mannose is most frequently found as α anomer. The atoms in this cyclic molecule then arrange themselves in space to minimize the amount of strain on each of the covalent bonds. Web independent of stereoisomerization, sugars in ring form of a given type (such as glucose) can “twist themselves into alternative conformations called boat and chair. This rotation produces either of.
Draw the a and b forms of glucose by moving the groups (h, oh, or ch,oh) to the appropriate positions for the hydroxy groups, make sure the bond on the ring is bonded to the oxygen, not the hydrogen. The atoms in this cyclic molecule then arrange themselves in space to minimize the amount of strain on each of the covalent bonds. Note that a new asymmetric centre is formed on cyclization, at c1. These two forms always exist in equilibrium. The process is catalyzed by acid, since hemiacetal formation is catalyzed by acid.
Web glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and the hydrogen atoms on the ring. A haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and the hydrogen atoms on the ring. Draw the α and β forms of glucose by moving the groups (h,oh, or ch2oh) to the appropriate positions.
The Process Is Catalyzed By Acid, Since Hemiacetal Formation Is Catalyzed By Acid.
Glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Web it is possible to obtain a sample of crystalline glucose in which all the molecules have the α structure or all have the β structure. Haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and the hydrogen atoms on the ring. This rotation produces either of.
The Rest Is One Of Two Cyclic Forms Of Glucose Formed When The Hydroxyl Group On Carbon 5 (C 5) Bonds To The Aldehyde Carbon 1 (C 1 ), As Shown Below.
Draw the a and b forms of glucose by moving the groups (h, oh, or ch,oh) to the appropriate positions for the hydroxy groups, make sure the bond on the ring is bonded to the oxygen, not the hydrogen. A haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and hydrogen atoms on the ring. Web glucose ring form and straight line form when glucose forms the ring structure, it can form two isomers. Draw the αα and the ββ forms of glucose by placing the groups (h,oh,or ch2oh)(h,oh,or ch2oh) in the appropriate positions.
Glucose Generally Exists In Ring (Cyclic) Form.
Draw the a and the b forms of glucose by placing the groups (h, oh, or ch,oh) in the appropriate positions. Hence glucose forms a six membered ring structurally similar to that of pyran, whilst fructose forms a five membered ring similar to furan. Web glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. Is the alpha or the beta form “really” glucose?
The Ring Form Is More Stable, But In Solution All Three Structures Are Present.
A haworth projection shows the orientations of the hydroxyl groups and hydrogen atoms on the ring. When we prepare solid glucose, we usually get either the alpha or the beta form of the. Note that this rearrangement does not change the relative positions of hydroxyl groups. These two forms always exist in equilibrium.