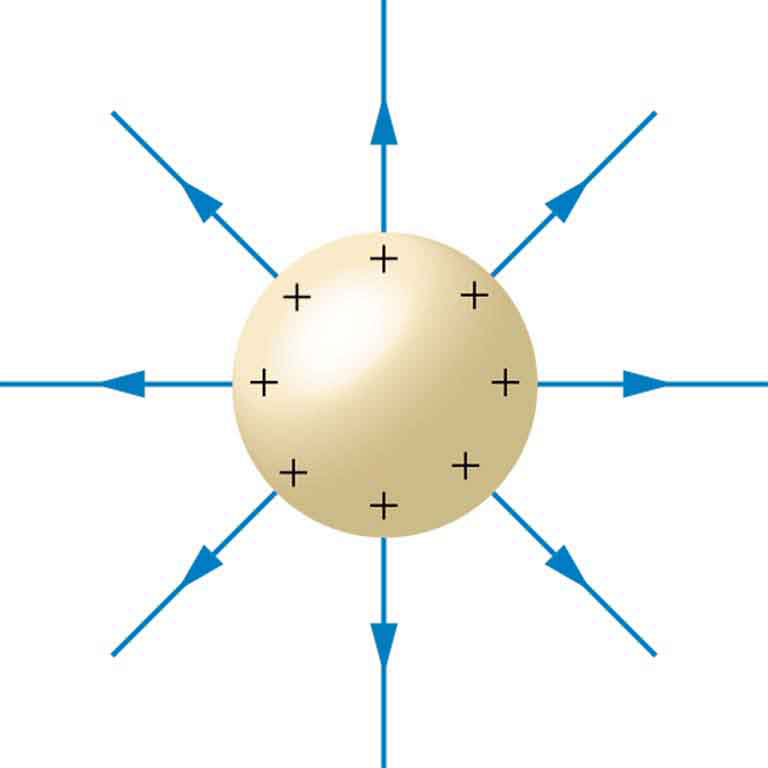
Electric Field Drawing
Electric Field Drawing - Web the electric field is often visualised using field lines, which are what you can see in the interactive demo at the top of the page. Electric field strength is a vector, and its direction is the direction in which a positive charge would be forced. All field lines are continuous curves or lines without breaks. We can think of the forces between charges as something that comes from a property of space. The electric field lines are parallel to the direction of force experienced by a positive test charge placed at that point. A useful means of visually representing the vector nature of an electric field is through the use of electric field lines of force. That property is called the electric field. Describe the properties of the electric field. Draw an arrow at each point where you place the test charge to represent the strength and the direction of. The number of field lines depends on the charge.
The video lesson answers the following questions: That, in essence, is what equation \ref{efield3} says. Then, you use the direction of the electric field lines to determine the direction of the force that would be experienced by a positive test charge placed in the field. The direction of the arrow shows the way a positive charge will be. Create models of dipoles, capacitors, and more! The electric field lines are parallel to the direction of force experienced by a positive test charge placed at that point. Basic conventions when drawing field lines.
In the next section, we describe how to determine the shape of an electric field of a source charge distribution and how to sketch it. A useful means of visually representing the vector nature of an electric field is through the use of electric field lines of force. Explain the purpose of an electric field diagram. Field lines go into negative charges. Fields are usually shown as diagrams with arrows:
Electric field lines follow a number of rules. We can reformulate the problem by breaking it into two distinct steps, using the concept of an electric field. Of a negative point charge with twice the magnitude of positive charge. Think of one charge as producing an electric field everywhere in space. Describe the properties of the electric field. Drawings using lines to represent electric fields around charged objects are very useful in visualizing field strength and direction.
Create models of dipoles, capacitors, and more! The field lines should never crossover. All field lines are continuous curves or lines without breaks. Then, you use the direction of the electric field lines to determine the direction of the force that would be experienced by a positive test charge placed in the field. Draw an arrow at each point where you place the test charge to represent the strength and the direction of.
Electric field strength is a vector, and its direction is the direction in which a positive charge would be forced. Think of one charge as producing an electric field everywhere in space. Electric field lines follow a number of rules. Web describe an electric field diagram of a positive point charge;
All Field Lines Are Continuous Curves Or Lines Without Breaks.
In the next section, we describe how to determine the shape of an electric field of a source charge distribution and how to sketch it. Web arrange positive and negative charges in space and view the resulting electric field and electrostatic potential. We can think of the forces between charges as something that comes from a property of space. Electric field lines follow a number of rules.
Describe The Properties Of The Electric Field.
The video lesson answers the following questions: A pattern of several lines are drawn that extend between infinity and the source charge or from a source charge to a second nearby charge. That property is called the electric field. Basic conventions when drawing field lines.
The Number Of Field Lines Originating Or Terminating At A.
Web at each location, measure the force on the charge, and use the vector equation e → = f → / q test e → = f → / q test to calculate the electric field. Charges shape the space around them, forming an electric field that interacts with other charges. The electric field lines are parallel to the direction of force experienced by a positive test charge placed at that point. Explain the purpose of an electric field diagram.
The Purpose Of This Section Is To Enable You To Create Sketches Of This Geometry, So We Will List The Specific Steps And Rules Involved In Creating An Accurate And Useful.
Web to draw electric field patterns, you start by identifying the charges that are present in the field. Then, you use the direction of the electric field lines to determine the direction of the force that would be experienced by a positive test charge placed in the field. When the field is stronger, the field lines are closer to each other. Think of one charge as producing an electric field everywhere in space.